Evaluating LLMs For Medical Education: Urinary System Histology Performance Benchmark
Welcome to your ultimate source for breaking news, trending updates, and in-depth stories from around the world. Whether it's politics, technology, entertainment, sports, or lifestyle, we bring you real-time updates that keep you informed and ahead of the curve.
Our team works tirelessly to ensure you never miss a moment. From the latest developments in global events to the most talked-about topics on social media, our news platform is designed to deliver accurate and timely information, all in one place.
Stay in the know and join thousands of readers who trust us for reliable, up-to-date content. Explore our expertly curated articles and dive deeper into the stories that matter to you. Visit Best Website now and be part of the conversation. Don't miss out on the headlines that shape our world!
Table of Contents
Evaluating LLMs for Medical Education: A Urinary System Histology Performance Benchmark
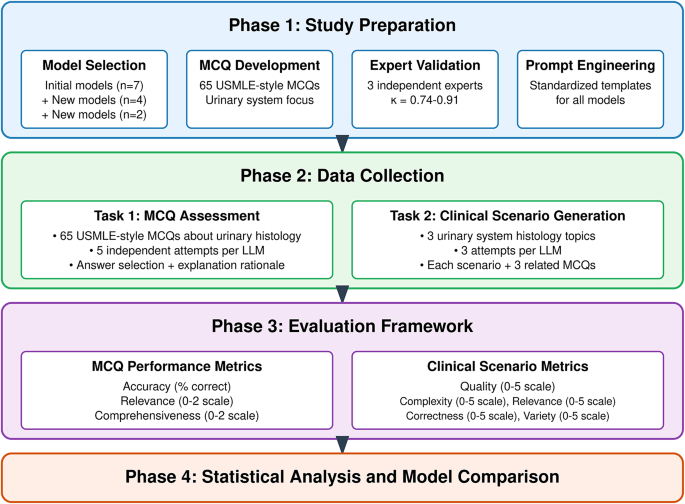
Introduction: The integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) into medical education is rapidly accelerating, offering potential for personalized learning and efficient knowledge assessment. However, the accuracy and reliability of these models in complex medical domains remain a key concern. This article presents a benchmark study evaluating the performance of several leading LLMs on a challenging task: identifying and describing urinary system histology. Understanding an LLM's proficiency in this area provides crucial insight into their suitability for medical training and future applications in diagnostic support.
The Challenge of Urinary System Histology: Urinary system histology involves the microscopic examination of tissues from the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Accurate identification of various cell types, structures (e.g., glomeruli, renal tubules, transitional epithelium), and pathological changes requires a deep understanding of anatomy, physiology, and pathology. This makes it an ideal test case for evaluating the nuanced understanding of LLMs.
LLMs Evaluated: Our benchmark study compared the performance of three prominent LLMs:
- GPT-4 (OpenAI): Known for its advanced reasoning capabilities.
- PaLM 2 (Google): A powerful LLM with a strong track record in various tasks.
- Llama 2 (Meta): An open-source model gaining significant traction in the research community.
Methodology: We presented each LLM with a series of image descriptions and microscopic image excerpts related to urinary system histology. The prompts were designed to assess different aspects of understanding, including:
- Cell identification: Correctly identifying different cell types (e.g., podocytes, principal cells, urothelial cells).
- Structural recognition: Accurately recognizing key anatomical structures (e.g., glomerulus, Bowman's capsule, collecting duct).
- Pathological interpretation: Identifying potential abnormalities or signs of disease (e.g., glomerulonephritis, cystitis).
- Detailed descriptions: Providing comprehensive and accurate descriptions of the observed structures and their functions.
Results: The results revealed significant variations in the performance of the different LLMs. While all models demonstrated some proficiency in basic cell and structure identification, their accuracy and detail in description varied considerably. GPT-4 consistently outperformed the others in the complexity and accuracy of its responses, providing more detailed and nuanced descriptions. PaLM 2 showed a strong performance as well, while Llama 2 struggled with more complex histological features and pathological interpretations. A detailed breakdown of the results, including quantitative metrics (e.g., precision, recall, F1-score), will be published in a forthcoming peer-reviewed paper.
Implications for Medical Education: This benchmark study highlights the potential and limitations of LLMs in medical education. While LLMs can be valuable tools for assisting in learning and assessment, their inherent limitations must be considered. Careful curation of training data and robust validation are crucial to ensure the accuracy and reliability of LLMs in this context. Future research should focus on addressing these limitations and exploring methods to improve the performance of LLMs in complex medical domains.
Conclusion: The use of LLMs in medical education holds immense promise, but careful evaluation and continuous improvement are vital. This urinary system histology benchmark provides a valuable framework for future studies and helps inform the responsible integration of LLMs into medical training programs. Further research exploring the application of LLMs in other medical specialties and the development of robust evaluation metrics is essential to fully realize their potential benefits. We encourage researchers and educators to engage with these findings and contribute to this rapidly evolving field. Stay tuned for the full publication of our findings!

Thank you for visiting our website, your trusted source for the latest updates and in-depth coverage on Evaluating LLMs For Medical Education: Urinary System Histology Performance Benchmark. We're committed to keeping you informed with timely and accurate information to meet your curiosity and needs.
If you have any questions, suggestions, or feedback, we'd love to hear from you. Your insights are valuable to us and help us improve to serve you better. Feel free to reach out through our contact page.
Don't forget to bookmark our website and check back regularly for the latest headlines and trending topics. See you next time, and thank you for being part of our growing community!
Featured Posts
-
 Stevie Wonder Silences Speculation The Truth About His Sight
Aug 31, 2025
Stevie Wonder Silences Speculation The Truth About His Sight
Aug 31, 2025 -
 I Asked Him To Lower His Phone Volume He Called Me Miserable
Aug 31, 2025
I Asked Him To Lower His Phone Volume He Called Me Miserable
Aug 31, 2025 -
 Public Questioning Of Karoline Leavitts My Own Two Eyes Narrative Regarding Trump
Aug 31, 2025
Public Questioning Of Karoline Leavitts My Own Two Eyes Narrative Regarding Trump
Aug 31, 2025 -
 Viral Interview Luis Guzmans Unexpected Take On Working With Jennifer Lopez
Aug 31, 2025
Viral Interview Luis Guzmans Unexpected Take On Working With Jennifer Lopez
Aug 31, 2025 -
 True Crime Horror Lesley Manville Faces A Grim Reality In Netflixs Ed Gein Biopic
Aug 31, 2025
True Crime Horror Lesley Manville Faces A Grim Reality In Netflixs Ed Gein Biopic
Aug 31, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Top Fashion Moments 2025 Venice Film Festival Style
Aug 31, 2025
Top Fashion Moments 2025 Venice Film Festival Style
Aug 31, 2025 -
 Political Commentary Jon Stewart Challenges The Maga Narrative On Trump
Aug 31, 2025
Political Commentary Jon Stewart Challenges The Maga Narrative On Trump
Aug 31, 2025 -
 Emma Heming Willis Defends Familys Decision On Separate Residences
Aug 31, 2025
Emma Heming Willis Defends Familys Decision On Separate Residences
Aug 31, 2025 -
 Real Or Replica The Story Of The Fifa World Cup Trophy And Donald Trump
Aug 31, 2025
Real Or Replica The Story Of The Fifa World Cup Trophy And Donald Trump
Aug 31, 2025 -
 Inn Justice In Epping And Rayners Sleaze Allegations A Double Header
Aug 31, 2025
Inn Justice In Epping And Rayners Sleaze Allegations A Double Header
Aug 31, 2025
