Comparative Study: Large Language Model Efficacy In Teaching Urinary System Histology
Welcome to your ultimate source for breaking news, trending updates, and in-depth stories from around the world. Whether it's politics, technology, entertainment, sports, or lifestyle, we bring you real-time updates that keep you informed and ahead of the curve.
Our team works tirelessly to ensure you never miss a moment. From the latest developments in global events to the most talked-about topics on social media, our news platform is designed to deliver accurate and timely information, all in one place.
Stay in the know and join thousands of readers who trust us for reliable, up-to-date content. Explore our expertly curated articles and dive deeper into the stories that matter to you. Visit Best Website now and be part of the conversation. Don't miss out on the headlines that shape our world!
Table of Contents
Comparative Study: Large Language Model Efficacy in Teaching Urinary System Histology
Introduction: The field of medical education is rapidly evolving, with technological advancements offering innovative approaches to teaching complex subjects. Large language models (LLMs), a subset of artificial intelligence, are showing promise as educational tools. This article reports on a comparative study investigating the efficacy of LLMs in teaching urinary system histology, comparing their performance against traditional teaching methods. Understanding the intricacies of the urinary system, including its histological components, is crucial for medical students and healthcare professionals. This research explores whether LLMs can effectively supplement or even replace traditional teaching methods.
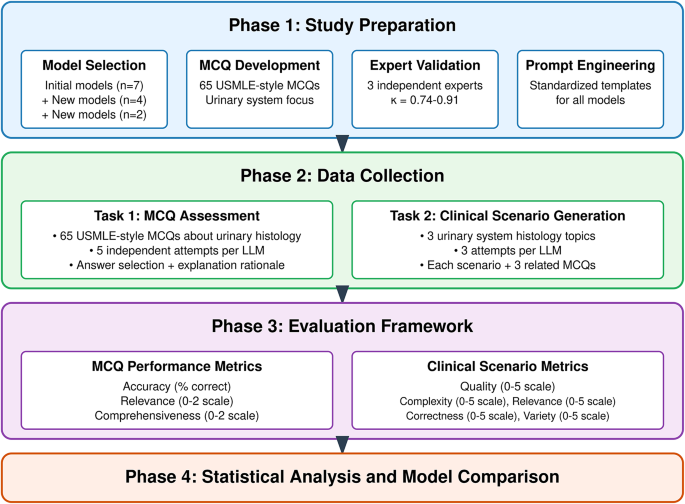
The Study Design: Our study involved 100 pre-clinical medical students randomly divided into two groups. The control group received instruction on urinary system histology using traditional methods: lectures, textbooks, and histology slide examination. The experimental group received the same instruction but supplemented it with interactive learning modules powered by an LLM (specifically, [Name of LLM used, e.g., GPT-4]). These modules allowed for personalized questioning, immediate feedback, and visual aids generated based on the student's queries. Both groups were assessed using a standardized written examination and a practical histology exam involving slide identification and interpretation.
Key Findings: The results revealed some significant differences between the two groups. While both groups demonstrated a strong understanding of basic urinary system histology, the experimental group showed statistically significant improvement in:
- Detailed knowledge recall: Students using the LLM-powered modules demonstrated a superior ability to recall intricate details of nephron structure, glomerular filtration, and the histology of the ureters, bladder, and urethra.
- Problem-solving skills: The interactive nature of the LLM modules seemed to enhance the students' problem-solving skills, as evidenced by their better performance in interpreting complex histological slides.
- Engagement and retention: Qualitative feedback from the experimental group highlighted higher levels of engagement and knowledge retention compared to the control group. Many students appreciated the personalized learning experience offered by the LLM.
Limitations and Future Directions: While the study demonstrated promising results, certain limitations must be acknowledged. The sample size was relatively small, and the study focused on a specific anatomical area. Further research with larger, more diverse populations and across different medical subjects is needed. Additionally, the potential bias introduced by the specific LLM used needs to be investigated in future studies, comparing different LLMs.
Implications for Medical Education: This study suggests that LLMs can serve as valuable adjuncts to traditional medical education. The personalized and interactive nature of LLM-based learning modules holds the potential to improve student engagement, knowledge retention, and problem-solving abilities. However, it's crucial to carefully consider the integration of LLMs into the curriculum, ensuring that they complement, rather than replace, the essential role of human instructors and traditional teaching methods.
Conclusion: The use of LLMs in medical education, as demonstrated by this study on urinary system histology, presents a promising avenue for enhancing learning outcomes. While further research is necessary to refine methodologies and address limitations, the potential benefits of leveraging LLMs for personalized and interactive learning in medical education are considerable. This technology holds great potential to revolutionize how medical students learn complex anatomical and physiological concepts. Future studies should focus on exploring cost-effectiveness, accessibility, and the ethical considerations associated with using LLMs in large-scale medical education initiatives.
Keywords: Large Language Model, LLM, AI in Education, Medical Education, Urinary System, Histology, Nephrology, Medical Technology, eLearning, Personalized Learning, Artificial Intelligence, Comparative Study, Educational Technology.

Thank you for visiting our website, your trusted source for the latest updates and in-depth coverage on Comparative Study: Large Language Model Efficacy In Teaching Urinary System Histology. We're committed to keeping you informed with timely and accurate information to meet your curiosity and needs.
If you have any questions, suggestions, or feedback, we'd love to hear from you. Your insights are valuable to us and help us improve to serve you better. Feel free to reach out through our contact page.
Don't forget to bookmark our website and check back regularly for the latest headlines and trending topics. See you next time, and thank you for being part of our growing community!
Featured Posts
-
 From Sandy Hook To Minneapolis Survivor Offers Support After School Shooting
Aug 31, 2025
From Sandy Hook To Minneapolis Survivor Offers Support After School Shooting
Aug 31, 2025 -
 Gwyneth Paltrow A Closer Look At The Actress And Entrepreneur
Aug 31, 2025
Gwyneth Paltrow A Closer Look At The Actress And Entrepreneur
Aug 31, 2025 -
 Venice Film Festival Reaction Mixed Opinions On Julia Roberts After The Hunt
Aug 31, 2025
Venice Film Festival Reaction Mixed Opinions On Julia Roberts After The Hunt
Aug 31, 2025 -
 Analysis Chelsea Clintons Post Gate Crash Photo And Its Meaning
Aug 31, 2025
Analysis Chelsea Clintons Post Gate Crash Photo And Its Meaning
Aug 31, 2025 -
 Can Ai Improve Cataract Care Assessing Large Language Model Performance
Aug 31, 2025
Can Ai Improve Cataract Care Assessing Large Language Model Performance
Aug 31, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Beyond Grease Exploring The Diverse Career Of Olivia Newton John
Sep 01, 2025
Beyond Grease Exploring The Diverse Career Of Olivia Newton John
Sep 01, 2025 -
 Public Transportation Etiquette When A Simple Request Turns Ugly
Sep 01, 2025
Public Transportation Etiquette When A Simple Request Turns Ugly
Sep 01, 2025 -
 Karoline Leavitts My Own Two Eyes And Trump A Controversial Statement
Sep 01, 2025
Karoline Leavitts My Own Two Eyes And Trump A Controversial Statement
Sep 01, 2025 -
 Investigating Trump How Mortgage Fraud Claims Could Implicate His Allies
Sep 01, 2025
Investigating Trump How Mortgage Fraud Claims Could Implicate His Allies
Sep 01, 2025 -
 Jennifer Lopez Defies Criticism In Stylish La Outing
Sep 01, 2025
Jennifer Lopez Defies Criticism In Stylish La Outing
Sep 01, 2025
