Comparative Study: Large Language Model Accuracy In Assessing Urinary System Histology For Medical Training
Welcome to your ultimate source for breaking news, trending updates, and in-depth stories from around the world. Whether it's politics, technology, entertainment, sports, or lifestyle, we bring you real-time updates that keep you informed and ahead of the curve.
Our team works tirelessly to ensure you never miss a moment. From the latest developments in global events to the most talked-about topics on social media, our news platform is designed to deliver accurate and timely information, all in one place.
Stay in the know and join thousands of readers who trust us for reliable, up-to-date content. Explore our expertly curated articles and dive deeper into the stories that matter to you. Visit Best Website now and be part of the conversation. Don't miss out on the headlines that shape our world!
Table of Contents
Comparative Study: Large Language Model Accuracy in Assessing Urinary System Histology for Medical Training
Revolutionizing Medical Education: AI's Role in Histopathology Analysis
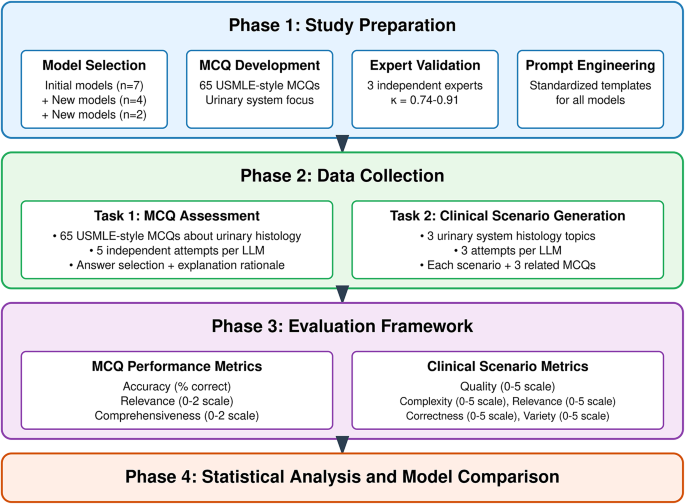
The field of medical education is undergoing a significant transformation, fueled by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI). One area ripe for disruption is the assessment of microscopic images, such as those used in urinary system histology. A recent comparative study has explored the accuracy of different Large Language Models (LLMs) in analyzing these images, offering exciting potential for enhancing medical training and diagnostics. This article delves into the key findings of this groundbreaking research and its implications for the future of pathology education.
The Challenge of Histopathology Assessment
Histopathology, the microscopic examination of tissues, plays a critical role in diagnosing various diseases, including those affecting the urinary system. Accurate interpretation of histological slides requires extensive training and expertise, often taking years to master. The process is time-consuming, subjective, and can vary between pathologists. This variability necessitates robust training methods to ensure consistency and accuracy in diagnosis. Traditional methods rely heavily on experienced instructors and a limited number of readily available case studies.
LLMs: A New Tool for Medical Education
Large Language Models, such as GPT-3 and others, are showing remarkable promise in various fields, including image analysis. This study sought to determine the potential of LLMs in assisting medical students and residents in learning to interpret urinary system histology. The researchers compared the accuracy of several LLMs in identifying key features and diagnosing pathologies within microscopic images of kidney, bladder, and ureter tissues. This involved training the models on a large dataset of annotated images, a process crucial for AI's learning and performance.
Key Findings of the Comparative Study
The study revealed significant variations in the accuracy of different LLMs. Some models demonstrated surprisingly high accuracy in identifying specific cellular structures and diagnosing common urinary tract conditions like glomerulonephritis and bladder cancer. However, the study also highlighted areas where LLMs struggled, particularly in distinguishing subtle features or identifying rare pathologies. Furthermore, the research underscored the importance of the quality and quantity of training data – more comprehensive datasets consistently resulted in improved LLM performance.
-
Strengths of LLM-based Assessment:
- Increased accessibility to diverse case studies.
- Potential for faster and more consistent feedback for students.
- Opportunity for personalized learning pathways.
- Reduced reliance on instructor time for basic image analysis.
-
Limitations of Current LLM Applications:
- Dependence on high-quality annotated training datasets.
- Potential for bias introduced through the training data.
- Inability to replace the judgment and experience of human pathologists.
- Need for further research to address limitations and improve accuracy.
Implications for the Future of Pathology Education
This comparative study provides valuable insights into the potential of LLMs to revolutionize medical education, specifically in the field of histopathology. While LLMs are not ready to replace human experts, their ability to assist in training and provide rapid feedback could significantly improve the learning experience for medical students. Future research should focus on improving the accuracy of LLMs in handling complex cases and mitigating potential biases in training data. The integration of LLMs into digital pathology platforms could ultimately enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of medical training programs worldwide.
Call to Action: Further research and development in this area are crucial to fully unlock the potential of LLMs in medical education. Collaboration between AI developers, pathologists, and educators is vital to creating robust and reliable tools that benefit both students and patients. Learning more about AI's role in medicine is paramount for healthcare professionals looking to stay at the forefront of innovation. [Link to relevant medical education resources]

Thank you for visiting our website, your trusted source for the latest updates and in-depth coverage on Comparative Study: Large Language Model Accuracy In Assessing Urinary System Histology For Medical Training. We're committed to keeping you informed with timely and accurate information to meet your curiosity and needs.
If you have any questions, suggestions, or feedback, we'd love to hear from you. Your insights are valuable to us and help us improve to serve you better. Feel free to reach out through our contact page.
Don't forget to bookmark our website and check back regularly for the latest headlines and trending topics. See you next time, and thank you for being part of our growing community!
Featured Posts
-
 Elie Honig Deconstructs Trumps Potential For National Guard Deployment
Aug 31, 2025
Elie Honig Deconstructs Trumps Potential For National Guard Deployment
Aug 31, 2025 -
 The Ed Gein Story Monster And The Birth Of Horrors Darkest Icons
Aug 31, 2025
The Ed Gein Story Monster And The Birth Of Horrors Darkest Icons
Aug 31, 2025 -
 No Cost Review Conducted By Ministers Before English Council Mergers
Aug 31, 2025
No Cost Review Conducted By Ministers Before English Council Mergers
Aug 31, 2025 -
 Emma Heming Willis Addresses Criticism Of Bruce Willis Caregiving
Aug 31, 2025
Emma Heming Willis Addresses Criticism Of Bruce Willis Caregiving
Aug 31, 2025 -
 U S Inflation Update June Consumer Prices Show Projected Rise
Aug 31, 2025
U S Inflation Update June Consumer Prices Show Projected Rise
Aug 31, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Free Daily Horoscope Monday September 1 2025
Sep 01, 2025
Free Daily Horoscope Monday September 1 2025
Sep 01, 2025 -
 The Closing Of Alligator Alcatraz A Look At Life Inside
Sep 01, 2025
The Closing Of Alligator Alcatraz A Look At Life Inside
Sep 01, 2025 -
 Childrens School Success The Critical Role Of The First Week
Sep 01, 2025
Childrens School Success The Critical Role Of The First Week
Sep 01, 2025 -
 Gta 6 Pc Release System Requirements Character Roster And Indian Pricing
Sep 01, 2025
Gta 6 Pc Release System Requirements Character Roster And Indian Pricing
Sep 01, 2025 -
 John Deeres Commitment To Sustainability B30 Biodiesel Adoption Expands
Sep 01, 2025
John Deeres Commitment To Sustainability B30 Biodiesel Adoption Expands
Sep 01, 2025
